Significant of Environmental health and safety (EHS) - Requirements of EHS in Solar PV
Health and safety is a very important aspect of any workplace as it protects the well being of employers, customers and visitors. It also make good business sense as workplace which neglect health and safety processes may lose staff and may increase costs and profitability. Health refers to the general well being of a person in which there is a sense of mental, physical and social well being. Safety is a feeling of security in which a person can work without danger or injury. As the world is not an ideal place and people suffer injuries and accidents occur at work. Proper health and safety equipments and procedures can help in eliminating such problems to a great level.
Deployment of solar PV System has been ever increasing globally and in India. All the components of a Solar PV System are subjected to rigorous safety and solar testing protocols at the time of manufacturing and complies the various IEC and other international codes and standards for safety. In spite of all this, due to many factors like poor designing and installation or negligence in O & M, there are different risks associated with PV System which has to be mitigated. This article explains the different hazards associate with solar roof top power plants and the best practices to be followed in order to prevent any accidents at Solar Power Plant Site. The intention of the article is to create awareness among the different stakeholders of solar roof top power plant which includes solar developers, operational staff, house owners and individuals in the vicinity of rooftop power plant.

Why EHS in work places required
The benefits of maintaining a health and safety standard in the organization are as follows
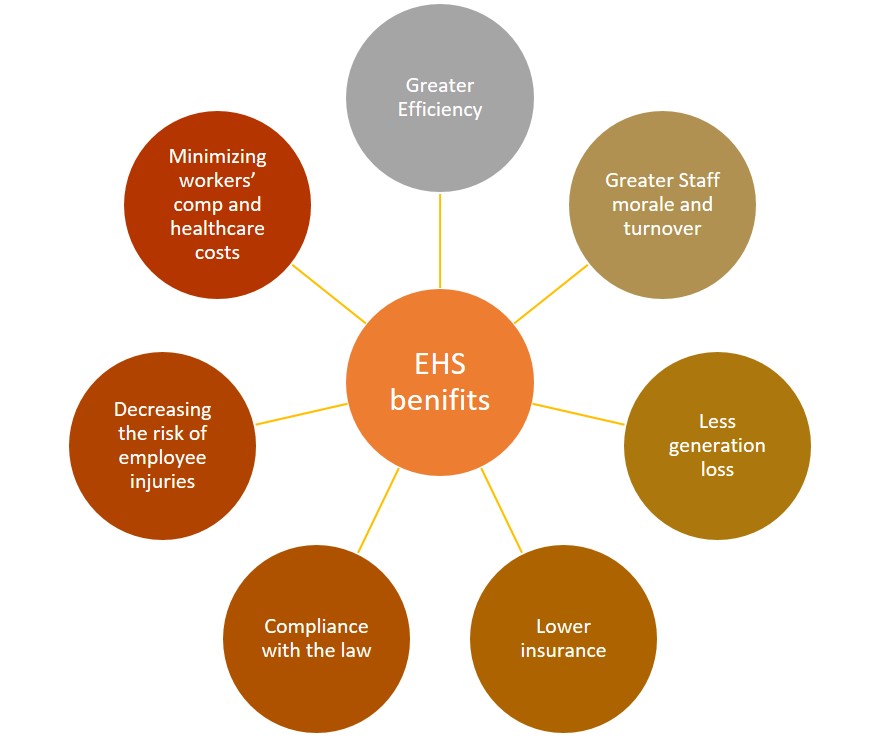
Accidence in work places can cost money in different ways. Some of the cost factors are energy loss due to shut down of plants, lost wages, medical treatment, damage to equipment and stock etc. The other major implications include loss of reputation, penalties due to generation variation, staff recruitment difficulty etc.
Health of the workers has a direct influence on Productivity at work. Poor occupational health and reduced working capacity of the workers may cause an economic loss of 10-20% of GNP. WHO estimates that only 10-15% of workers have access to basic occupational health services. The burden of disease attributed to occupational diseases is high and it is estimated to be about 11 million cases annually, with about 7,00,000 deaths. In Indian scenario unsafe work practices are one of the leading cause of death and disability among the working population. As per the data released by ILO (International Labour Organization), it is estimated that around 4,03,000 people die in India every year due to work related problems i.e. about 46 every hour. By applying proper EHS measures this can be prevented.
Types of accidents in Indian industries
The frequency rate of accident occurrence in India has showing an upward trend. As per Ministry of Labour and Employment, Govt of India, standard reference note states 1,141 numbers of fatal injuries and 25,173 numbers nonfatal injuries in factories in 2014. Some of the different types of accidents which occurred in the construction industry during 2013 and 2014 has been shown in the table given below:
Table 1: Types of accidents in construction industry (lndia)
|
Type of accidents in industries |
Years |
|
|
2013 |
2014 |
|
|
Fall from height |
12,803 |
15,399 |
|
Factory/Machine Accidents |
955 |
797 |
|
Accidental Fire |
22,177 |
19,513 |
|
Electrocutions |
10,218 |
9,606 |
|
Heat/Sun Stroke |
1,216 |
1,248 |
|
Lightning |
2,833 |
2,582 |
|
Accidental Explosion |
449 |
1,194 |
Involvement of EHS in Solar PV industry
Proper implementation of EHS is playing vital role in reducing OSH (occupational Safety and Health) problems to an extent. Compared to other electricity generation technologies mortality rate seems to be less in Solar PV. While considering Table 2 in case of solar rooftop is facing high mortality rate than other RE sources.
Table 2: Morality rate in electricity generation sector
|
Energy source |
Mortality rate (in deaths/PWh) |
Percentage of energy type |
Year |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Coal (global) |
100000 |
41% (electricity) |
2012 |
|
Coal (China) |
170000 |
75% (electricity) |
2012 |
|
Coal (US) |
10000 |
32% (electricity) |
2012 |
|
Oil |
36000 |
33% (total energy) |
2012 |
|
8% (electricity) |
|||
|
Natural Gas |
4000 |
22% (electricity) |
2012 |
|
Biofuel/biomass |
24000 |
21% (total energy) |
2012 |
|
Solar - rooftop |
440 |
2012 |
|
|
Wind |
150 |
2% (electricity) |
2012 |
|
Wind (UK) |
<1000 |
3.81% (electricity) |
2011 |
|
Hydro (global) |
1400 |
16% (electricity) |
2012 |
|
Hydro (US) |
5 |
6% (electricity) |
2012 |
|
Nuclear (global) |
90 |
17% (electricity) |
2012 |
|
Nuclear (US) |
0.1 |
19% (electricity) |
2012 |
Involvement of EHS in solar PV can be divided as follows
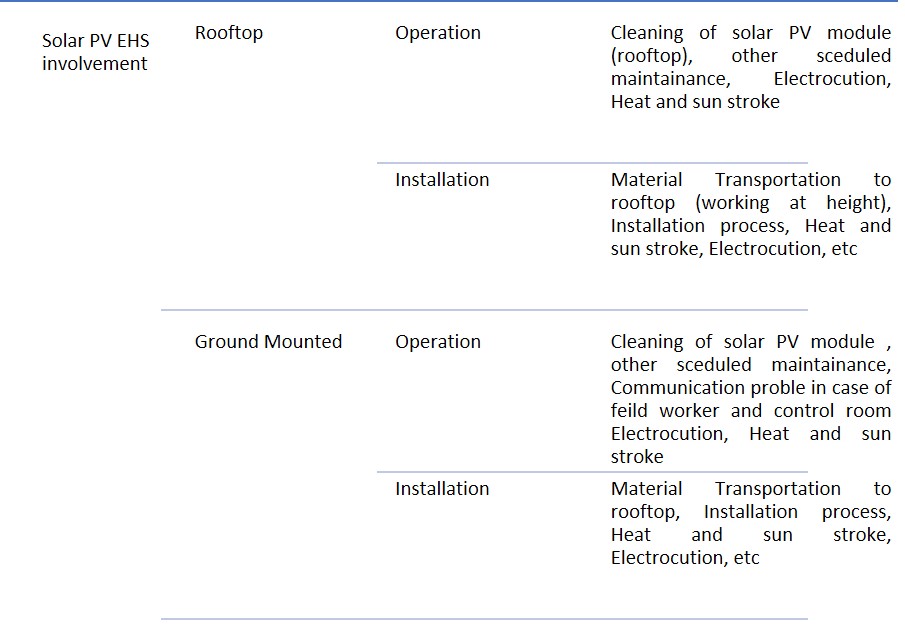
Some of the factors affecting EHS in solar PV sector as follows

The cost associated WHS (Workplace Health and Safety) failure has also to be taken into consideration. These are all the avoided costs due to adverse events that are prevented by OSH interventions. Understanding all the potential risks and failure which can heavily cost the organization can also play as an important element in justifying the business case for investing in better EHS systems and practices.
Cost associated with EHS failure can take into consideration the following factors
Direct Cost:
- Compensation claims cost - Explanation (1 or 2 sentences)
- Increased insurance premium cost- Explanation (1 or 2 sentences)
Indirect Cost:
- Employee responses - absenteeism, 'presenteeism' and turnover.
- Training a new employee is also an indirect cost associated
- Cost of Generation loss and lost time
- Cost of Personnel and time allocated to investigating and writing up the accident, work re-organization and follow-up costs of administration
- Litigation expenses and fines
- Plant and equipment repairs cost
- Additional wage costs, sick pay and temporary labour replacement costs
- Cost due to greater public scrutiny
- Reduced shareholder value
- Overhead cost of spare capacity maintained in order to absorb the cost of accidents
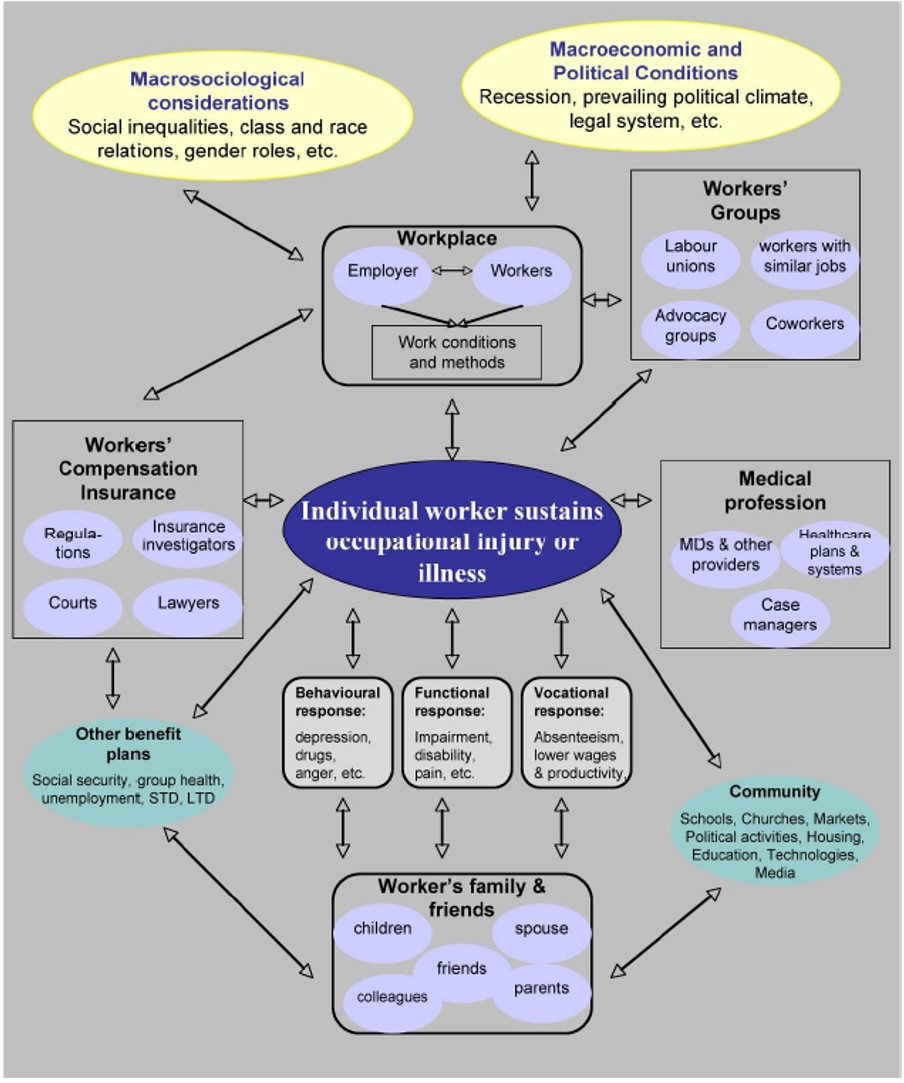
The relationship between injured workers and all other groups can be brief in the following figure
Source : Page 33 Benosh Report : Socio economic Costs of Accidents
Cost factors involved in EHS
Cost of investment mainly consists of initial investments and recurring costs
- Initial Investment includes purchasing (as a one-off) new equipment and materials. This also includes planning, preparation and installation
- Training of employee which includes external trainer or consultant fees and working time spent by employees on training
- Maintenance costs of equipment
- Periodic training costs.
The costs of all preventive activities at company level
|
Cost Variable |
Description |
|
Initial Investment |
Cost of all safety equipment's |
|
Additional investments |
Changes made in the existing structure or construction to facilitate functioning of OSH equipment ( Eg. Reconstruction, removal of existing less safer system etc.) |
|
Engineering, consultancy and planning costs related to investments |
Cost associated with internal and external activities for design, documentation, implementation of new equipment or working procedures |
|
Recurring costs of Purchase of personal protective equipment |
This includes costs of protective equipment considering no. of times they have to be replaced in their life time |
|
Recurring maintenance costs |
Maintenance costs of safety equipment's |
|
Extra work time of employees |
Time spent on meetings, training, safety inspections, drills, participatory developments |
|
In-company activities |
Human resource management, health promotion, OSH policy and management |
About Project
Under USAID- PEER cycle 5, World Institute of Sustainable Energy has done research study to strategizing O&M and performance evaluation of solar PV power plants in India. Project team has visited more than 100 power plants all across India and done exhaustive study on national and international best practices, standards ... Ream More
Useful Links
Articles by Subject
Our Contact
Plot No.44, Hindustan Estates,
Kalyani Nagar, Pune 411 006, India
(020) 26613855
(020) 26613832